In February 2025, Google Maps officially turned 20 years old—a milestone that highlights two decades of innovation in digital navigation. What started in 2005 as a basic online mapping tool has since evolved into an indispensable platform powered by AI, real-time data, and immersive technologies. From everyday commuters to global travelers and businesses, millions rely on Google Maps to navigate the world with ease.
As we celebrate this anniversary, let’s take a look back at the key innovations that have shaped Google Maps, transforming it from a simple mapping service into a powerful tool that redefines how we explore and connect with our surroundings.
1. The Birth of Google Maps
When Google Maps launched in February 2005, it set out to solve a simple yet crucial problem: making digital maps more interactive and user-friendly. Unlike the static, image-based maps of the past, Google Maps introduced seamless scrolling, zooming, and an intuitive search function. This innovation marked a major shift in how people accessed geographic information online.
Originally developed as a C++ desktop program by Danish brothers Lars and Jens Eilstrup Rasmussen, Google acquired the technology in 2004 and transformed it into a web-based application. By integrating satellite imagery, street data, and powerful search capabilities, Google Maps quickly became the go-to platform for navigation.
The launch laid the foundation for what would become a continuously evolving mapping ecosystem—one that would soon go beyond simple directions to offer real-time insights, business listings, and immersive geographic experiences.
2. Google Earth: The World in 3D
Shortly after launching Google Maps, Google introduced Google Earth in 2005, revolutionizing how people explore the world. Unlike traditional 2D maps, Google Earth provided a three-dimensional, satellite-based view of the planet, allowing users to zoom in on cities, landmarks, and remote locations with remarkable detail.
Built on Keyhole Inc.’s Earth Viewer—a technology Google acquired in 2004—Google Earth combined satellite imagery, aerial photography, and geographic data to create an immersive, interactive experience. Over time, it expanded to include topographical features, street overlays, and even historical imagery, enabling users to track changes in landscapes, urban development, and environmental shifts over the years.
Beyond navigation, Google Earth became a powerful tool for education, urban planning, and scientific research. Scientists monitored climate change, historians reconstructed ancient cities, and educators transformed geography lessons into virtual journeys.
This groundbreaking innovation set the stage for the next major leap in mapping technology: real-time traffic navigation.
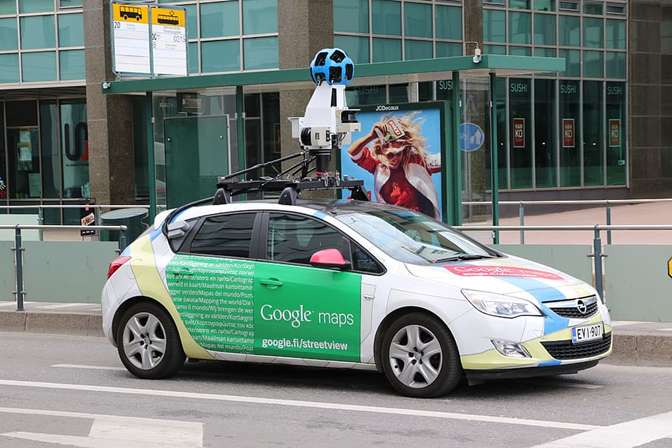
3. Street View: A Ground-Level Perspective
In 2007, Google introduced Street View, a feature that brought a 360-degree, street-level view of cities and landmarks directly to users. By mounting cameras on cars, bikes, and even backpacks, Google captured panoramic images of streets worldwide, allowing people to virtually explore neighborhoods as if they were walking through them.
Street View quickly became more than just a navigation tool. It allowed users to preview destinations, explore unfamiliar areas, and even revisit past locations with historical imagery. Over time, it expanded to include indoor views of businesses, natural landmarks, and remote locations, making it a valuable resource for travel, real estate, and urban planning.

4. Real-Time Traffic: Smarter, Faster Routes
In 2007, Google Maps introduced real-time traffic data, revolutionizing how drivers navigate congestion. By analyzing anonymized location data from mobile devices, Google could detect traffic slowdowns and suggest faster alternate routes.
Over time, the system improved with AI predictions and user reports, making traffic estimates more accurate and rerouting more efficient. This breakthrough set the stage for the next major advancement: turn-by-turn navigation.
5. Turn-by-Turn Navigation: Changing the Way We Drive
In 2009, Google Maps introduced turn-by-turn navigation, making standalone GPS devices nearly obsolete. With voice-guided directions, automatic rerouting, and real-time traffic updates, users could drive with confidence, without needing to manually check maps.
This innovation turned smartphones into full-fledged navigation systems, continuously improving with live traffic data, lane guidance, and offline maps. By combining precision with ease of use, turn-by-turn navigation became an essential feature, changing the way millions travel daily.
Next, Google Maps set its sights on helping businesses connect with local customers.
Stay Forward
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
6. Google My Business: Empowering Local Businesses
In 2014, Google launched Google My Business (GMB), transforming how businesses manage their online presence. Instead of relying on third-party directories, businesses could now claim their listings, update information, and engage with customers directly through Google Maps and Search. Ranking high in search results became more important than ever, as businesses appearing in top positions saw significantly more visibility, customer engagement, and foot traffic. For years, DAC has been helping businesses achieve this, ensuring they stand out in an increasingly competitive local search landscape.
GMB provided essential tools like business hours, photos, reviews, and real-time updates, making it easier for customers to connect with local stores, restaurants, and service providers. Over time, features like booking integrations, messaging, and insights turned GMB into a powerful marketing tool, reinforcing Google Maps as a key player in local commerce.
In 2021, Google rebranded GMB as Google Business Profile (GBP), integrating it more deeply into Maps and Search for a streamlined experience. But businesses weren’t the only ones shaping Google Maps—users also played a key role in keeping it accurate and up to date.
7. Local Guides: The Power of Crowdsourced Insights
To keep Google Maps accurate and dynamic, Google introduced the Local Guides program in 2015. This initiative encouraged users to contribute reviews, photos, and edits, enriching the platform with firsthand insights about businesses and locations.
By rewarding contributors with points, badges, and early access to new features, Google fostered a global community of users dedicated to improving map accuracy. Their input helped businesses gain visibility, provided travelers with reliable recommendations, and ensured Maps remained a trusted resource for local information.
8. Immersive View: The Future of Digital Mapping
In 2023, Google introduced Immersive View, a groundbreaking feature that combined AI, real-time data, and 3D mapping to create hyper-realistic previews of locations. By layering Street View, aerial imagery, and predictive models, Immersive View allowed users to explore cities with unprecedented detail before visiting in person.
This technology provided more than just static images—it integrated weather conditions, traffic patterns, and lighting changes to give users a dynamic, real-time sense of their destination. Whether planning a trip, checking out a new restaurant, or navigating a busy urban area, Immersive View enhanced the way people interact with maps.
9. AI and Google Maps: The Next Chapter
By 2025, Google Maps had fully integrated AI-driven insights, making navigation more intuitive than ever. With the introduction of Gemini AI, the platform could now provide personalized route suggestions, smarter location recommendations, and enhanced augmented reality (AR) overlays for real-world exploration.
AI-powered features also improved search accuracy, real-time traffic predictions, and eco-friendly routing, helping users make more informed travel decisions. As machine learning continues to advance, Google Maps is evolving into a truly intelligent assistant, offering tailored experiences based on user preferences and real-time conditions.
10. 20 Years of Innovation—What’s Next?
Over the past two decades, Google Maps has evolved from a simple digital map into a powerful, AI-driven platform that shapes how people navigate the world. With innovations like real-time traffic updates, turn-by-turn navigation, Street View, and Immersive View, it has redefined the way we explore cities, connect with businesses, and plan our journeys.
As technology continues to advance, the future of Google Maps will likely bring even deeper AI integration, real-time augmented reality, and smarter urban navigation. Whether it’s hyper-personalized recommendations, enhanced sustainability features, or seamless smart city mapping, one thing is certain—Google Maps will keep pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Happy 20th anniversary, Google Maps! Here’s to the next two decades of innovation.
Contributing Experts
Explore more insights

Stay Forward
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
