
 Click-fraud-2
Click-fraud-2 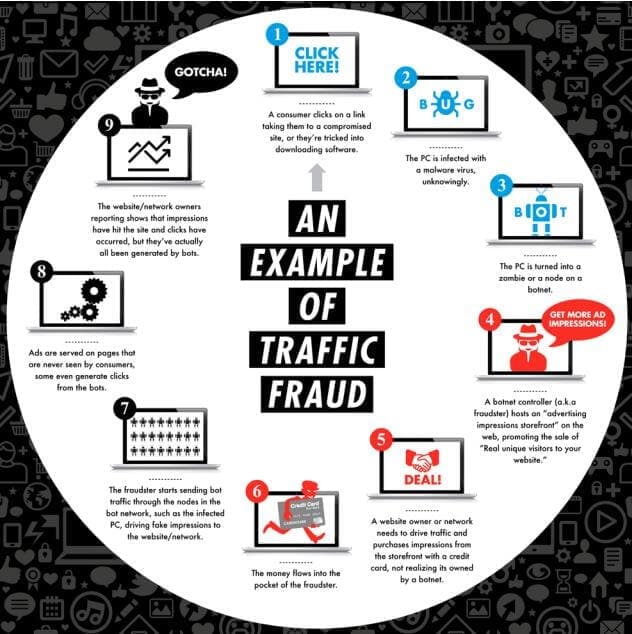
Recently, a number of DAC clients have expressed concern around Click Fraud and the impacts, if any, it could have on their media programs. I remember in the early 2000s, long before automated PPC bid management was in play, having my own concerns around click fraud and actively monitoring campaigns to see if there really was anything to be concerned about. The reality was, and is, YES. Click fraud does happen and is something to be aware of across all paid media channels. In fact, earlier this year, Ziff Davis’ CEO called fraud the biggest threat to today’s online advertising business, and industry surveys are uncovering that bots will waste $11.6 billion of global advertising spend this year.
What is Click Fraud?
The simplest way to describe click fraud is repeated human or non-human clicks on a particular ad with the intention of either increasing publisher revenue or placing an advertiser (usually a competitor) at a disadvantage by inflating their click count, decreasing their conversion rate and increasing their media spend.
The two most likely ways fraudulent clicks are generated include:
1. Manual clicking (sometimes outsourcing clickers or using click farms that generate fake Facebook Likes, Twitter followers and YouTube views). Unethical, yes. Illegal, not yet. And,
2. Through automated means; according to comScore, 36% of media traffic today is generated by machines, not humans. Software designed to behave similar to humans (also known as Bots) has been known to affect online registrations, voting, commenting and sharing. Viruses like Mevade and Sefnit that attack Microsoft systems even include components capable of performing click fraud.
The results:
- More publisher revenue, and loss of advertiser trust in that publisher
- Increased advertiser spend from falsely inflated click rates
- Higher CPC (and ultimately Cost Per Lead) due to the seemingly increase in demand
- Decreased conversion rates from an influx of ad clicks that don’t convert, and
- The appearance of an ineffective media program
How to address click fraud?
Publishers are aware of click fraud and many actively take steps to address it. For example, Google’s Ad Traffic Quality Resource Center provides details on Invalid Click Protection and ensures advertisers are not charged for fraudulent clicks or invalid traffic. Google has also recently acquired Spider.io, a UK company that helps advertisers and publishers ensure ads are being seen by humans.
In addition, when Facebook advertisers were targeted with click fraud a couple of years ago, an engineering director on Facebook`s ad team described a number of steps and processes their growing security and safety staff take to identify and address invalid ad clicks, including filtering bot clicks, identifying low value (double or repetitive) clicks, and monitoring click activity over a period of time.
IAB has a number of suggestions on how to address traffic fraud (a combo of click and impression fraud).
 Image Source: iab.net
Image Source: iab.net
- Here are some suggestions on what you, as an advertiser, can do to address click fraud:
- Educate yourself, this two-pager from the IAB is a good start.
- Monitor your campaigns closely and regularly, if you see a sudden spike in paid clicks or if impressions appear significantly more than your potential audience size, it’s probably worth investigating.
- Work with media partners who have earned your trust.
- Our primary recommendation: take a performance-focused approach to paid media. Define media goals and objectives, and implement tactics that take end actions into consideration, like Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) or Cost Per Lead (CPL) campaigns. In doing so, you`re not relying on impressions and clicks to successfully meet your goals; you’re focused on generating tangible conversions and paying only for those conversions. You’re also holding your media partners accountable for conversion delivery.

